Drug Eruption and Hepatitis Induced by Antituberculosis Therapy: A Case Report
A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33005/jdiversemedres.v2i10.275Keywords:
Drug eruption, Hepatitis, Hepatotoxicity, Antituberculosis drugs, TuberculosisAbstract
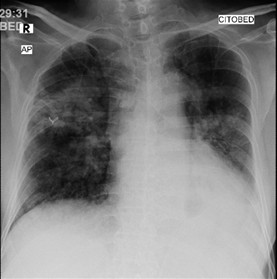
Pulmonary tuberculosis remains a global health issue, with one of the challenges being the adverse side effects of anti-tuberculosis drugs that can interfere with the success of therapy. This case reports a 67-year-old man with pulmonary tuberculosis who experienced a rifampicin-induced drug eruption and pyrazinamide-induced hepatitis during first-line antituberculosis combination therapy. After temporarily discontinuing the antituberculosis regimen, the patient was given supportive therapy with corticosteroid and antihistamine for the drug eruption, and stronger neo-minophagen C injections for the hepatitis. After stabilization, the regimen was adjusted to a combination of isoniazid and ethambutol, and streptomycin was added as the third agent; however, due to an allergic reaction, streptomycin was replaced with levofloxacin. The new regimen, isoniazid-ethambutol-levofloxacin, combined with appropriate management of the adverse reactions resulted in favorable clinical outcomes, marked by the disappearance of the itchy red rash on the face and body, improvement in liver function as seen from liver enzymes and bilirubin levels, and a stable general condition. This case report emphasizes the importance of being aware of the adverse side effects of antituberculosis regimens, especially in elderly patients. Regular monitoring of liver function, early detection of drug reactions, and safe and individualized regimen adjustments are important strategies to prevent complications without compromising the success of tuberculosis treatment. This case provides important lessons regarding a cautious, evidence-based clinical approach to addressing serious side effects of antituberculosis drugs.
Downloads
References
Natarajan A, Beena PM, Devnikar AV, Mali S. A systemic review on tuberculosis. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis. 2020;67(3):295–311.
Irmawati A, Sihombing MR, Darmawan AR, Al Khonsa N, Faizah Balqis N, Zakia F, et al. A Review: Cigarettes Trigger Chronic Inflammation in the Body. International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research and Studies. 2025;5(3):1337–45.
Wikurendra EA, Nurika G, Tarigan YG, Kurnianto AA. Risk Factors of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Countermeasures: A Literature Review. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2021;9(F):549–55.
Bagcchi S. WHO’s Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. The Lancet Microbe. 2023;4(1):e20.
Saktiawati AMI, Probandari A. Tuberculosis in Indonesia: challenges and future directions. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2025;13(8):669–71.
Suárez I, Fünger SM, Kröger S, Rademacher J, Fätkenheuer G, Rybniker J. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis. Deutsches Ärzteblatt international. 2019;116:729–35.
Nagarajan S, Whitaker P. Management of adverse reactions to first-line tuberculosis antibiotics. Current Opinion in Allergy & Clinical Immunology. 2018;18(4):333–41.
Prasad R, Singh A, Gupta N. Adverse Drug Reactions with First-Line and Second-Line Drugs in Treatment of Tuberculosis. ANAMS. 2021;57(01):16–35.
Caraux-Paz P, Diamantis S, De Wazières B, Gallien S. Tuberculosis in the Elderly. JCM. 2021;10(24):5888.
Kwon BS, Kim Y, Lee SH, Lim SY, Lee YJ, Park JS, et al. The high incidence of severe adverse events due to pyrazinamide in elderly patients with tuberculosis. Ehtesham HS, editor. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(7):e0236109.
Campbell JR, Trajman A, Cook VJ, Johnston JC, Adjobimey M, Ruslami R, et al. Adverse events in adults with latent tuberculosis infection receiving daily rifampicin or isoniazid: post-hoc safety analysis of two randomised controlled trials. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2020;20(3):318–29.
Ernst M, Giubellino A. Histopathologic Features of Maculopapular Drug Eruption. Dermatopathology. 2022;9(2):111–21.
Chen CB, Abe R, Pan RY, Wang CW, Hung SI, Tsai YG, et al. An Updated Review of the Molecular Mechanisms in Drug Hypersensitivity. Journal of Immunology Research. 2018;2018:1–22.
Mereškevičienė R, Danila E. The Adverse Effects of Tuberculosis Treatment: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Medicina. 2025;61(5):911.
Katran ZY, Bulut I, Babalik A, Keren M. Treatment and Management of Hypersensitivity Reactions Developed Against Anti-Tuberculosis Drug. The International Journal of Mycobacteriology. 2022;11(3):309–17.
Afida AI, Widiatma RR. Drug Eruption Due to Antituberculosis Drugs: A Case Report. NJ. 2025;9(2):333–42.
Shaker G, Mehendale T, De La Rosa C. Fixed Drug Eruption: An Underrecognized Cutaneous Manifestation of a Drug Reaction in the Primary Care Setting. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e28299.
Ren Z, Peng J, Yan T, Chen J, Zhu N, Li G. Analysis of Clinical Differences in Drug-Induced Hepatitis in Elderly Patients Caused by Various Drugs. Hepat Mon. 2024;24(1):e146984.
Xu Y, Jiang Y, Li Y. Pyrazinamide enhances lipid peroxidation and antioxidant levels to induce liver injury in rat models through PI3k/Akt inhibition. Toxicology Research. 2020;9(3):149–57.
Cao J, Mi Y, Shi C, Bian Y, Huang C, Ye Z, et al. First-line anti-tuberculosis drugs induce hepatotoxicity: A novel mechanism based on a urinary metabolomics platform. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2018;497(2):485–91.
Huang W, Lin Y, Kuo H, Sheu M, Feng Y, Feng I, et al. Benefits of stronger Neo‐Minophagen C in acute hepatitis after transarterial chemoembolization therapy for hepatomas. Adv in Digestive Medicine. 2023;10(1):8–14.
Husna AK, Nurhidayati IN. Diagnosis, Tata Laksana, dan Prognosis Hepatitis A. Proceeding Book Call for Papers Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta. 2024;52–8.
Dartois VA, Rubin EJ. Anti-tuberculosis treatment strategies and drug development: challenges and priorities. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(11):685–701.
Gill CM, Dolan L, Piggott LM, McLaughlin AM. New developments in tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment. Breathe. 2022;18(1):210149.
Rocha DMGC, Viveiros M, Saraiva M, Osório NS. The Neglected Contribution of Streptomycin to the Tuberculosis Drug Resistance Problem. Genes. 2021;12(12):2003.
Childs-Kean LM, Shaeer KM, Varghese Gupta S, Cho JC. Aminoglycoside Allergic Reactions. Pharmacy. 2019;7(3):124.
Dillard LK, Martinez RX, Perez LL, Fullerton AM, Chadha S, McMahon CM. Prevalence of aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss in drug-resistant tuberculosis patients: A systematic review. Journal of Infection. 2021;83(1):27–36.
Espinosa-Pereiro J, Sánchez-Montalvá A, Aznar ML, Espiau M. MDR Tuberculosis Treatment. Medicina. 2022;58(2):188.
Vanino E, Granozzi B, Akkerman OW, Munoz-Torrico M, Palmieri F, Seaworth B, et al. Update of drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment guidelines: A turning point. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2023;130:S12–5.
He Y, Li X. The treatment effect of Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, and Gatifloxacin contained in the conventional therapy regimen for pulmonary tuberculosis: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine. 2022;101(38):e30412.
Zhu C, Liu Y, Hu L, Yang M, He ZG. Molecular mechanism of the synergistic activity of ethambutol and isoniazid against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2018;293(43):16741–50.
Babu R, Vidya B, Roberts NS, Bhargavi. Efficacy of Levofloxacin as an Add-On Drug to Antitubercular Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients Complicated with Type II Diabetes. European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine. 2025;15:75–80.
Luo P pei, Wu L, Liu F, Tian Y hong, Chen L yin, Liu Y lin. Clinical efficacy of chemotherapy regimen combined with Levofloxacin in patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis complicated with Type-2 Diabetes. Pak J Med Sci. 2023;39(2).
Oh AL, Makmor-Bakry M, Islahudin F, Ting CY, Chan SK, Tie ST. Adverse drug reactions of first-line antitubercular drugs: A retrospective study on characteristics, management, factors, and impacts. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine. 2024;17(10):456–64.
Quddus MA, Tahir R, Munawar R, Kiani RS, Qazi N, Jehangir T. Risk factor for Rifampicin, Isoniazid and Pyrazinamide induced Hepatitis in Pulmonary Tuberculosis patients. Pakistan Journal of Chest Medicine. 2022;28(1):31–8.
Molla Y, Wubetu M, Dessie B. Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Induced Hepatotoxicity and Associated Factors among Tuberculosis Patients at Selected Hospitals, Ethiopia. HMER. 2021;13:1–8.
Resende LSO, Santos-Neto ETD. Risk factors associated with adverse reactions to antituberculosis drugs. J bras pneumol. 2015;41(1):77–89.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Diverse Medical Research : Medicosphere

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






